Mon, Jan 30, 2017
Native App vs Web App: Choosing the Right Path

Do you want to develop a mobile application? You can either create a native application or a web application. Even if you know absolutely nothing about IT development, this is an important choice because it determines your strategic positioning and the next steps of mobile project management. Let’s explain the main differences to make the right choice.
Understanding Native Apps and Web Apps
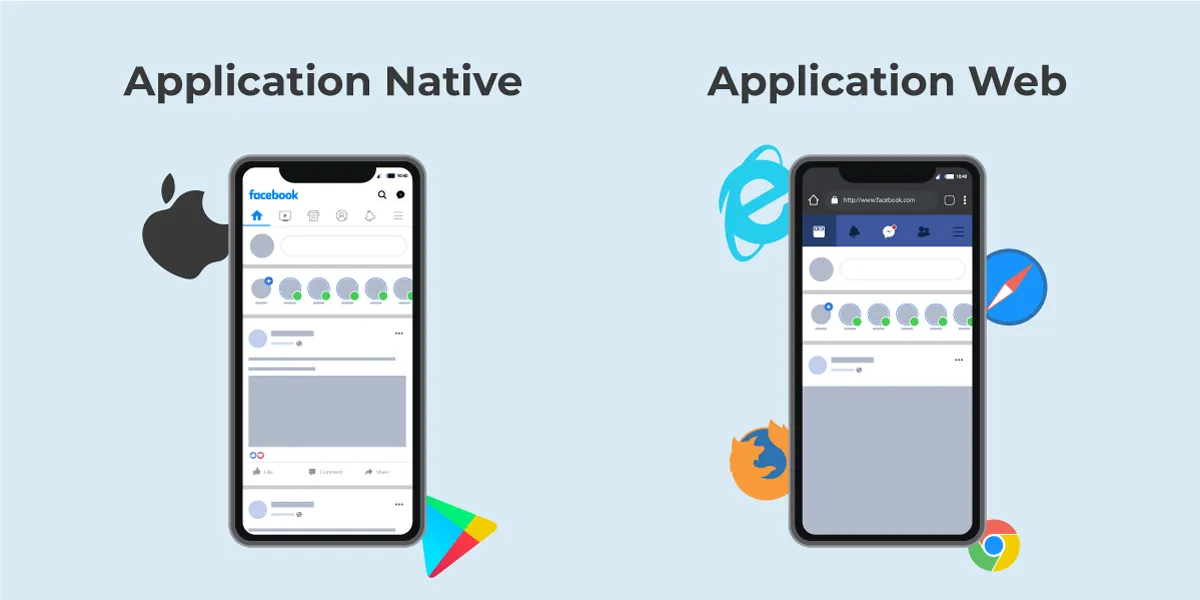
A native app is a software developed to meet the technical specifications of devices (iOS, Android, Windows, MacOS) and is installed directly on the user’s device. It can be consulted without an internet connection. The native app is often downloaded from app stores, but it is also possible to easily distribute native applications outside of the stores.
A web app is a lightweight and optimized website designed for mobile devices. It has a reduced size and, if possible, tactile functionality. Nowadays, web apps are mainly created using HTML5 to take advantage of the latest technological advances.
The Progressive Web App (PWA) is the latest major breakthrough in web apps: it combines the best features between the native application and the web app.
Comparing Native Apps and Web Apps
Accessibility and distribution
The main advantage of the web app is accessibility: the user consults it directly from a browser (Chrome, Safari, Internet Explorer…). He can navigate between different sites and consult the web app in a smooth and seamless way.
The native application is more constraining: the user must download it on his device beforehand. After downloading, it can be consulted offline from the user’s smartphone or tablet.
The Progressive Web App is browser-based, with no prior download, but can then be viewed offline through caching and the use of service workers.
Performance and User Experience
The native application is faster and more responsive than the web app because it is developed directly in the native language of each platform (iOS, Android, or Windows), instead of the web standard. This allows for access to specific features of the phone and tablet, such as the phonebook, camera, and GPS, which can be complicated from a web application.
In terms of ergonomics, the native application runs in full screen and has its own interface. The web app is located in a browser and it is not always possible to hide the navigation elements (address bar at the top…), except with the Progressive Web App (PWA) which allows you to add its icon from the home screen.
Marketing
When we talk about applications, we often think of the App Store and Google Play. That’s why native applications tend to be easier to find!
Nevertheless, the web app benefits from powerful search engine optimization, a privileged source of traffic. But beware, the App Store Optimization (ASO) revolutionizes this trend by allowing the integration of application content in Google’s referencing.
The strength of the native application lies in push notifications: these messages sent directly to users to alert them of updates draw their attention to new features.
Updates and maintenance
When choosing between web and native applications, the simplicity of updates often makes web apps more appealing. For developers, updates and maintenance of native apps can be a headache in terms of organization and budget. Fortunately, with PandaSuite, you can develop your own multi-platform application without needing to know how to code, and updates are instantaneous!
Development process
The development of a web app is generally less expensive than that of a native application because of the technologies used and the time required. That’s without counting on PandaSuite, which allows you to develop a native iOS, Android and HTML5 application without any line of code and for a very affordable budget.
In terms of planning, the native application often requires a quote on the App Store and Google Play, a process that can be costly and time consuming for developers.
Making the Right Choice
With PandaSuite, it becomes as easy and affordable to create a native application as a web app or Progressive Web App.
What you should ask yourself is:
- Performance: how important is execution speed and user experience within your application?
- Accessibility: Do you want your application to be accessible offline? Or should it be directly accessible from a website?
- Features: Do you want to use native features (such as a smartphone camera, etc.)?
- Marketing: How do you want to promote your application?
- Monetization: Do you want to monetize your app in the future?
The native versus web debate is a classic of its kind. The Progressive Web App reconciles the best of both worlds, the web since access to a PWA is via a browser, without downloading, and the best of the native app thanks to its icon on the home screen and its offline access!