Tue, Feb 3, 2026
What Is SCORM and What Is It Used For?

SCORM comes up constantly in e-learning projects. People call it a “format,” a “file,” or a “module.” It gets lumped in with tracking, reporting, and compliance.
No wonder there’s so much confusion.
Behind the acronym lies a technical standard designed to let training content communicate with a Learning Management System (LMS). Not a course type, not an authoring tool, not a display technology. Just a shared convention between your module and your platform.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- What SCORM actually is and how it works
- Its main use cases in e-learning projects
- Its strengths and limitations
What Is SCORM?
SCORM stands for Sharable Content Object Reference Model. It defines two things:
- Packaging: how to bundle learning content so an LMS can import it
- Communication: how that content sends tracking data back to the LMS during use
Think of it as a contract. Your e-learning module agrees to speak a certain way, and the LMS agrees to listen. When both sides follow the rules, everything works.
The output is usually a ZIP file, which is why people often say “SCORM file.” But the ZIP is just the wrapper. The real value is in the communication protocol inside.
What Does SCORM Do in an E-Learning Project?
SCORM became the de facto standard because it solves two core needs: ensuring LMS compatibility and making learning measurable.
1. Launch a Module from an LMS
Learners click a course in their LMS, and it just works. SCORM tells the LMS where to find the entry point and how to run the content. No custom integration required.
2. Track Completion, Score, and Time
The heart of SCORM is tracking. In most real-world projects, the data you actually capture includes:
| Data point | What it tells you |
|---|---|
| Completion status | Finished or not finished |
| Pass/fail | Met the threshold or not |
| Score | Quiz or assessment results |
| Time spent | Duration in the module |
| Bookmarking | Where to resume if they come back |
SCORM can technically report more, but it’s not an advanced analytics tool. It’s designed to prove that training was completed, not to analyze every micro-interaction.
3. Centralize Reporting
Once modules are in the LMS, teams can aggregate results by population, time period, or business unit. That’s especially useful for audit trails and regulatory compliance.
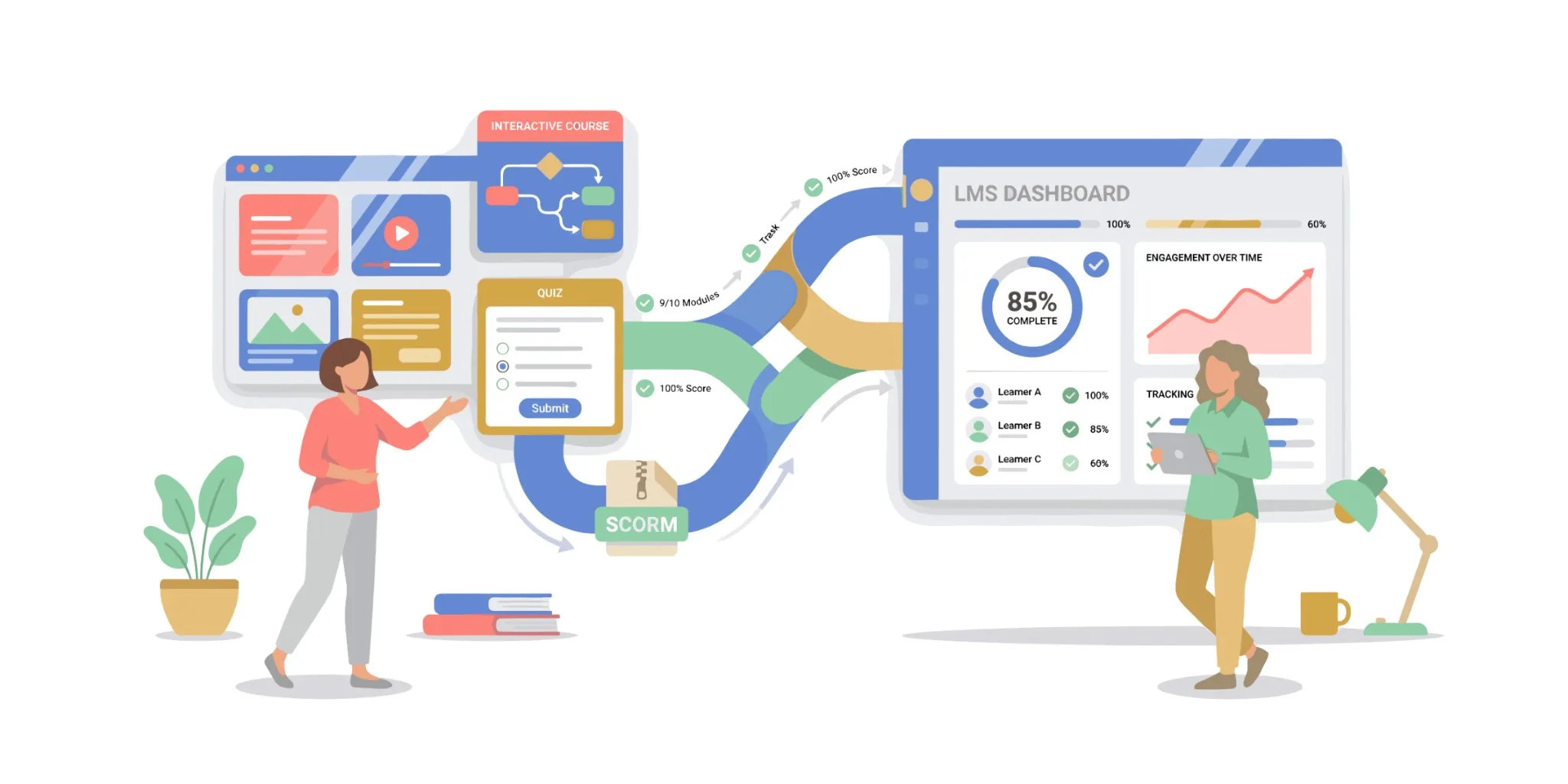
How a SCORM Package Works
Here’s a simple analogy:
- The SCORM package is a book
- The LMS is the library
- The SCORM standard is the rule that lets the library open the book and know if it’s been read
From Authoring Tool to ZIP
The workflow is always the same:
- Build your content in an authoring tool (Articulate Storyline, iSpring, PandaSuite, etc.)
- Set your SCORM options (version 1.2 or 2004, completion criteria)
- Hit export
- Upload the resulting ZIP file to your LMS
What’s Inside the ZIP
A SCORM package typically contains:
- Course files: HTML, JavaScript, media, etc.
- A manifest file:
imsmanifest.xml, which describes the content structure and metadata
The manifest is the index card for your book. Without it, the LMS doesn’t know what to do with your files.
How Content Talks to the LMS
Once launched, the module exchanges data with the LMS through a standardized interface called the SCORM API. The flow is simple:
- Module signals it’s starting
- Module sends progress or score updates
- Module reports a final status when complete
Key Concepts You’ll See Everywhere
Three terms come up constantly in SCORM projects:
| Concept | What it means |
|---|---|
| Completion | The module has been finished |
| Success | A threshold was met (score, validated quiz, etc.) |
| Bookmarking | The learner can resume a session later |
SCORM 1.2 vs SCORM 2004: Which One?
This question comes up on every project. In practice, the choice depends more on your LMS than on the standard itself.
| Criteria | SCORM 1.2 | SCORM 2004 |
|---|---|---|
| Compatibility | Nearly universal | Varies by LMS |
| Sequencing | Basic | Advanced (conditional navigation) |
| Tracking depth | Limited | More detailed |
| Complexity | Simple to implement | More complex |
| Adoption | Widespread | Uneven |
Our recommendation:
- SCORM 1.2 remains extremely widespread and offers near-universal compatibility.
- SCORM 2004 introduces additional features, especially around learning path sequencing, but support varies across platforms.
When in doubt, go with 1.2.
Strengths and Limitations of SCORM
Why It’s Still Around
SCORM continues to be widely used because it effectively addresses concrete needs: interoperability, compliance, and scalability for training programs.
It lets you standardize entire course catalogs and provide tracking evidence recognized in many regulatory contexts.
Where SCORM Falls Short
Step outside the “browser-based module inside an LMS” box, and limitations appear:
- Shallow tracking data
- Complex offline handling
- Inconsistent mobile behavior
- Heavy dependence on LMS implementation quality
SCORM remains solid in controlled environments, but less suited to distributed or multi-channel experiences.
Conclusion
SCORM remains a reliable standard when you need LMS-compatible modules and clear reporting. But it’s not a universal solution.
As projects grow in complexity or require deeper analytics, its limitations become apparent. Newer standards like xAPI or cmi5 can capture richer learning data and go beyond the LMS perimeter. In some cases, a simple web deployment with proper analytics tools may even be more appropriate than a SCORM package.
The right approach isn’t to automatically ask for “a SCORM.” Start with your actual use case, then choose the standard that best fits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is a SCORM file?
A ZIP package containing your e-learning module files (HTML, JavaScript, media) plus a manifest file (imsmanifest.xml) that describes the content structure to the LMS.
What’s the difference between SCORM and xAPI?
SCORM works exclusively inside an LMS and captures limited data (completion, score, time). xAPI can track learning experiences beyond the LMS: mobile, simulation, field activities, with much richer data.
Does my LMS support SCORM?
Most LMS platforms (Moodle, 360Learning, Cornerstone, Talentsoft, etc.) support SCORM 1.2. SCORM 2004 support is more variable. Check with your vendor.
Can I create SCORM content without coding?
Yes. Authoring tools like Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, iSpring, or no-code solutions like PandaSuite let you export SCORM packages without writing a line of code.