Tue, May 14, 2024
Rethinking Visitor Experience Through Digital Mediation

Today, more and more applications and digital media are appearing in museums. This trend has been strongly accentuated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Faced with the closure of their establishments and travel restrictions, cultural actors had to find innovative ways to maintain the connection with their audiences.
From virtual tours to interactive audio guides, including 3D modeling and touch kiosks, digital technology has emerged as an essential solution for continuing to offer enriching cultural experiences.
However, while digital technology represents a major challenge for museums today, many of these institutions are unsure how to approach it. Adopting new technologies can be complex and intimidating, especially for organizations with limited resources.
Indeed, producing quality digital content requires not only specific technical skills but also a deep understanding of the needs and expectations of the audiences. Small museums, in particular, face budget constraints and a lack of qualified personnel that hinder the implementation of ambitious digital projects.
Moreover, cultural mediation professionals regularly express concerns about the use of digital technology, fearing that it may replace direct interaction and human contact, essential elements of the traditional museum experience.
Caught between the lofty goals of ideal digitization, production challenges, a lack of technical knowledge, and fears of diluting cultural mediation, museums often move cautiously in this area.
Nevertheless, despite these obstacles, solutions exist to empower museums to imagine tomorrow’s mediation solutions in a simple, coherent, and controlled manner. Platforms and tools like PandaSuite democratize access to advanced technologies, offering museums of all sizes the opportunity to create immersive digital experiences without requiring advanced technical skills.
Attracting New Audiences Through Digital Technology
Digital technology first emerged as a solution to attract and engage a broader and more diverse audience in cultural institutions, particularly a younger audience. With COVID-19, museums had no choice but to develop digital strategies to maintain their connection with their audiences while their doors remained closed.
The Louvre Museum, for example, was one of the first to offer its collection interactively through virtual tours and social media. It attracted 10 million virtual visitors in two months during the lockdown.
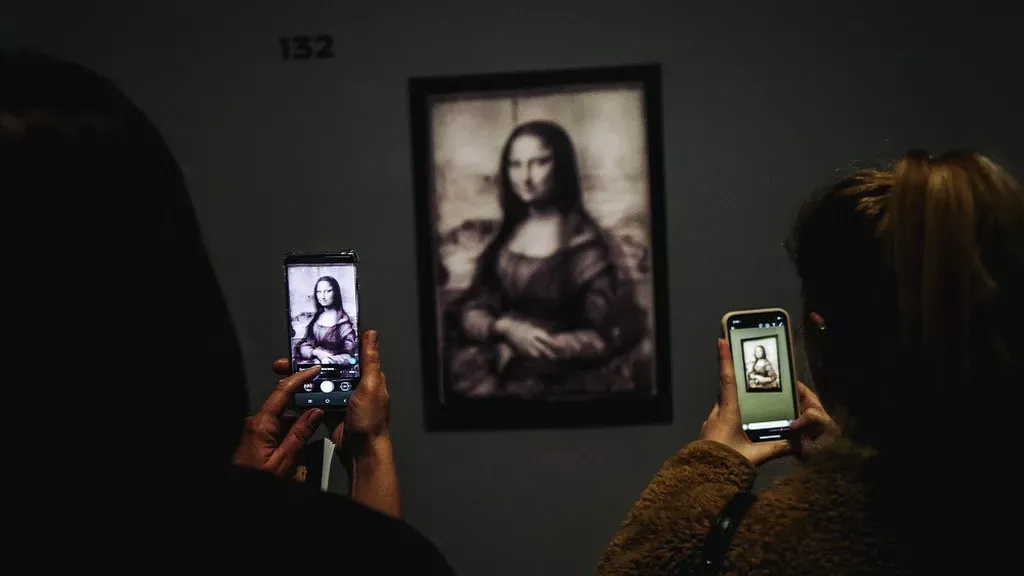

The virtual reality experience, “Face to Face with the Mona Lisa”
In recent years, museums, galleries, and cultural centers have continued to adopt digital solutions to make their collections more accessible and interactive. According to the Ministry of Culture, 1 in 2 museums now has a mobile application to assist with visits.
From mobile applications to virtual tours, interactive devices, and augmented reality exhibitions, digital technology is revolutionizing how the public interacts with cultural heritage. And this is not to mention the disruptions that Artificial Intelligence will bring in its wake.
Beyond cultural institutions, web giants have also entered the fray. Google’s mission is to disseminate culture to the widest audience possible. Since 2011, the Google Art Project has enabled virtual visits to 300 museums or sites worldwide through Street View technology and the 3D digitization of tens of thousands of artworks.
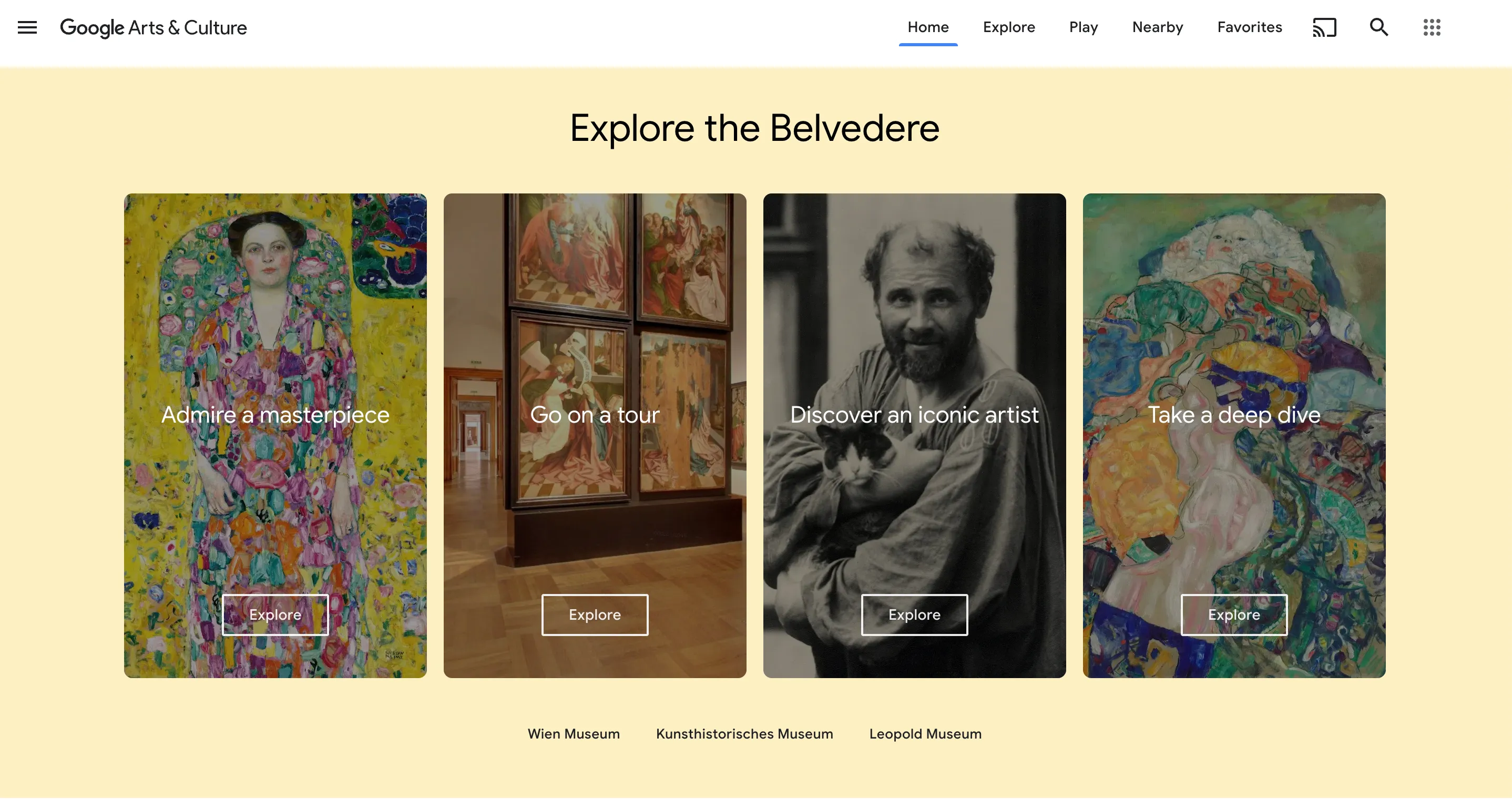
Google’s Arts & Culture project
The goals of digital mediation are varied and ambitious. It aims to broaden audiences by making culture more accessible and to increase visitor engagement, transforming a passive visit into an active experience. Additionally, integrating new technologies allows institutions to stay at the forefront of innovation, enhancing their reputation and image.
Fears of Diluting Cultural Mediation
Some cultural mediation professionals express concerns about the use of digital technology. Among the main concerns is the risk of dehumanizing the museum experience. For example, a visitor might focus on an application instead of directly admiring an artwork, thereby reducing direct interaction and valuable human contact with art.
They also worry about unequal access, knowing that some audiences, particularly older or economically disadvantaged individuals, might not have the necessary skills or technological means. The information overload and potential distraction caused by digital devices are also issues, as they might divert visitors’ attention from the artworks themselves.
Finally, there is the fear of rapid technological obsolescence and the high costs associated with updates and maintenance, which could represent a significant financial and logistical challenge for cultural institutions. These main concerns are generally reinforced by the fact that these actors feel disempowered by relying on external actors or heavy projects.
Challenges of Producing Digital Media
Indeed, producing digital media, whether an audio guide or a touch kiosk, presents numerous challenges in terms of resources, flexibility, and updates.
Small Cultural Organizations
For small cultural organizations, the main challenge lies in limited resources, both financial and human. For example, the cost of developing a custom mobile application can range from 10,000 to 50,000 euros, a sum often too high for museums with limited budgets.
The lack of qualified personnel in digital technologies (webmaster, web communication manager, multimedia production…) can also hinder the development of quality content.
Hiring an external developer or a development team to create specific applications or use the latest technologies can be prohibitive. Not to mention that managing and maintaining these technologies require continuously updated technical skills, representing an additional burden for small organizations.
Large Museums
Large museums, despite their greater resources, also face specific challenges in producing digital media. Although they often have larger budgets and qualified personnel, the complexity and scale of their collections require sophisticated and customized digital solutions, which can represent substantial costs.
Managing large databases and digitizing numerous artworks require a robust and scalable technological infrastructure. Additionally, large museums must maintain a high level of security to protect their data and visitors’ sensitive information. Integrating advanced technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) requires close coordination with external experts and significant investment in research and development.
Finally, large museums must constantly innovate to meet the expectations of a diverse and international audience, while preserving the authenticity and integrity of their physical exhibitions. This involves finding a balance between enriching the visitor’s digital experience and preserving the traditional museum experience.
Solutions for Producing Digital Media
Today, there are solutions to easily and economically produce applications and digital media.
With its intuitive no-code platform, PandaSuite democratizes access to advanced digital mediation tools, allowing small organizations to overcome technological barriers on a limited budget. Our platform offers the greatest creative freedom to create applications and digital mediation media: audio guide, mobile application, escape game, touch kiosk….
Users can easily integrate interactive and multimedia content, such as videos, animations, and virtual tours, enriching the visitor’s experience without requiring significant financial investment.
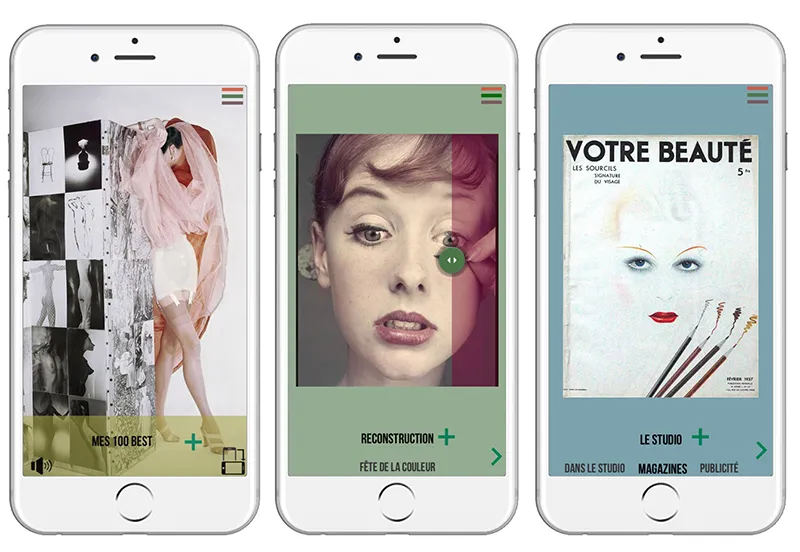
The Studio Blumenfeld application of the Cité de la Mode et du Design created with PandaSuite
Furthermore, the flexibility of PandaSuite allows museums and small heritage organizations to adapt their applications as new exhibitions are mounted or needs arise. This encourages a more agile and experimental approach, where institutions can test different digital mediation approaches to see what resonates best with their audience before committing to significant expenses.
Among other solutions to facilitate digital projects, museums can also benefit from collaborations with universities, design schools, and volunteer programs for technical and creative assistance.
Grants and specific funding for digital development, often available through public or private organizations, can provide additional resources.
Finally, continuous training of staff in basic digital skills and adopting a modular and scalable approach to developing media can maximize the efficiency and sustainability of digital initiatives.
The New Horizons of Digital Cultural Mediation
By reclaiming the subject, cultural actors see digital technology opening up unprecedented horizons for cultural mediation.
From increased interactivity to improved accessibility, these tools revolutionize our way of approaching culture. By adopting a balanced approach and judiciously integrating these technologies, museums can not only overcome current challenges but also create enriching experiences for future generations. The future of museums is digital, and it promises to be exciting.
Interactivity and Engagement
Digital tools create interactive experiences that captivate the public. For example, mobile applications can offer educational games based on a museum’s collections, while augmented reality technologies can overlay additional information on artworks, enriching the visit.
Accessibility and Inclusion
Digital technology makes culture more accessible. People with physical disabilities can enjoy virtual tours, while tools like subtitles and audio descriptions enhance the experience for the hearing or visually impaired. Additionally, digital content can be translated into multiple languages, making collections accessible to an international audience.
Education and Training
Digital platforms offer rich and diverse educational resources. Teachers can use applications and websites to integrate cultural elements into their lessons, and students can access interactive educational content that complements traditional learning.
Conservation and Dissemination
Digital technology plays a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage. Digitization technologies allow artworks and artifacts to be preserved in high resolution and widely disseminated through virtual exhibitions. This not only protects the originals but also shares these cultural treasures with a global audience.
Digital cultural mediation, initially perceived as a necessary constraint to attract a new audience, is an incredible opportunity to enrich and energize traditional cultural mediation.
At PandaSuite, we are convinced that digital technology does not replace the physical experience of culture but complements and significantly enriches it. By integrating digital technologies, we open new paths for engagement, accessibility, education, and conservation, redefining how we share and experience culture.
At PandaSuite, we have been supporting museums worldwide for over 10 years, providing them with the platform and expertise needed to successfully carry out their digital projects.